44 draw a dna nucleotide and an rna nucleotide label each of the 3 major parts
Unit 3 - Science 10 Learner’s Material - SlideShare Sep 09, 2015 · Use the patterns of the components of the DNA and RNA provided by your teacher. Color code phosphate = blue, deoxyribose sugar = green ,ribose sugar = brown and nitrogenous bases as follows: adenine = yellow, uracil = orange, guanine = violet, cytosine = red and amino acid = green. 2. Cut out the shapes of each nucleotide. 3. Nucleotide - Genome.gov Definition. A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
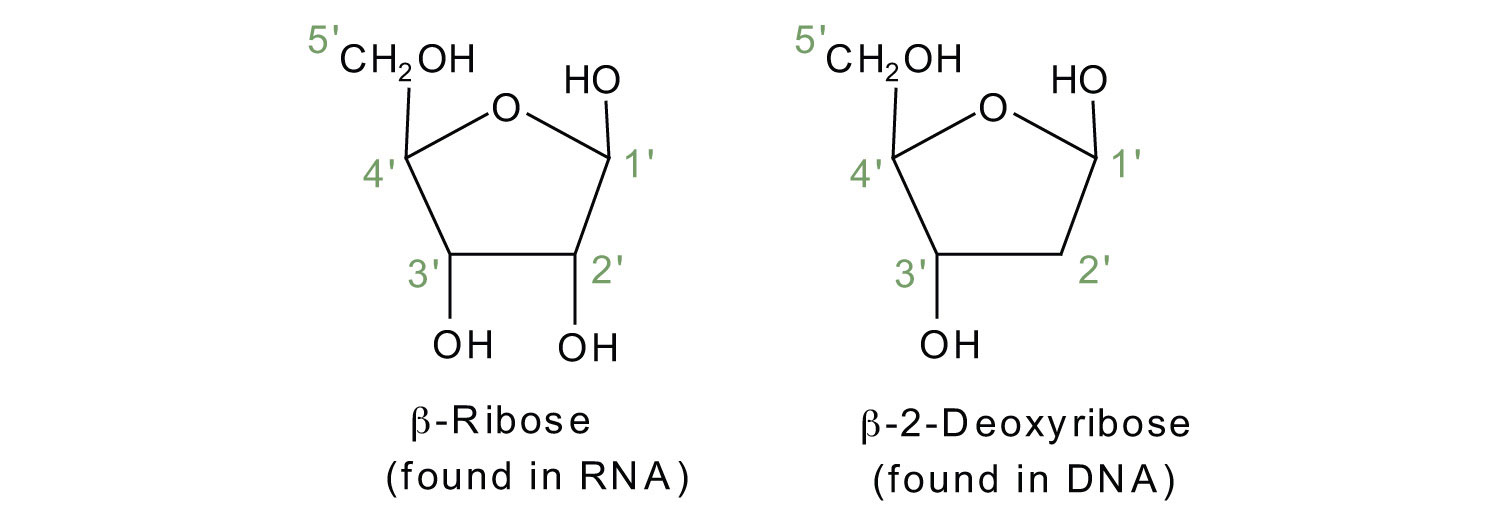
Difference Between DNA and RNA Nucleotides - Pediaa.Com What is a RNA Nucleotide. A RNA nucleotide is the monomer nucleotide found in RNA molecules. It contains ribose as the pentose monosaccharide, which is attached to a nitrogenous base at its 1′ carbon and a phosphate group at its 5′ carbon. Ribose contains two enantiomers: D-ribose and L-ribose. D-ribose is found in RNA.
Draw a dna nucleotide and an rna nucleotide label each of the 3 major parts
[Solved] 1. Draw a DNA nucleotide & an RNA nucleotide. Label each of ... 1. Draw a DNA nucleotide & an RNA nucleotide. Label each of the 3 major parts. This question was created from protein-synthesis-worksheet (3) Get more out of your subscription* Access to over 100 million course-specific study resources 24/7 help from Expert Tutors on 140+ subjects Full access to over 1 million Textbook Solutions Cell (biology) - Wikipedia This process involves the formation of new protein molecules from amino acid building blocks based on information encoded in DNA/RNA. Protein synthesis generally consists of two major steps: transcription and translation. Transcription is the process where genetic information in DNA is used to produce a complementary RNA strand. DOC Protein Synthesis Worksheet - Earland'S Class Resources Draw a DNA nucleotide & an RNA nucleotide. Label each of the 3 major parts. 2. What are the three major differences between DNA & RNA? 3. What is the . purpose of DNA replication? _____ 4. When & where does . replication. occur? ...
Draw a dna nucleotide and an rna nucleotide label each of the 3 major parts. DOC PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET - warrencountyschools.org The first step of protein synthesis is called Transcription. It occurs in the nucleus. During transcription, mRNA transcribes (copies) DNA. DNA is "unzipped" and the mRNA strand copies a strand of DNA. Once it does this, mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes into the cytoplasm. mRNA will then attach itself to a ribosome. Answered: Question #12 An actively respiring… | bartleby Jun 09, 2022 · Consider only the initial incorporation of carbon-14 in the first pass of labeled pyruvate through the citric acid cycle. [ draw the relevant structures that show how pyruvate is transformed to alpha-ketoglutarate. No mechanisms are required, but provide balanced equations. You do not need to draw the structures of cofactors] 12B. Understanding a Genome Sequence - Genomes - NCBI Bookshelf If a northern blot of cellular RNA is probed with a labeled fragment of the genome, then RNAs transcribed from genes within that fragment will be detected . Northern hybridization is therefore, theoretically, a means of determining the number of genes present in a DNA fragment and the size of each coding region. There are two weaknesses with ... PDF Structure Of DNA & RNA - Jiwaji University Three major forms: B-DNA A-DNA Z-DNA B-DNA is biologically THE MOST COMMON It is a -helix meaning that it has a Right handed, or clockwise, spiral. Complementary base pairing • A-T • G-C Ideal B-DNA has 10 base pair per turn(360o rotation of helix) So each base is twisted 36o relative to adjacent bases.
PDF LAB: MODELING TRANSCRIPTION & TRANSLATION PERIOD: (Adapted from POGIL ... Please put a box around 1 nucleotide of RNA and another box around 1 nucleotide of DNA. d. List 3 major STRUCTURAL differences between RNA and DNA: ... Draw and color each below. Label the 3 parts of each nucleotide. RNA Nucleotide DNA Nucleotide 5. Build 12 RNA nucleotides, using a variety of bases. ... PDF "unzipped" and the mRNA strand copies a strand of DNA. Once it does ... 1) Draw a DNA nucleotide & an RNA nucleotide. Label each of the 3 major parts. 2) What are three major differences between DNA & RNA? 3) What is the point of DNA replication? 4) When & where does replication occur? 5) What is the point of transcription? 6) What are three nucleotides together called on mRNA? (ie: ACA Draw a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide label each of the 3 major parts 1. Using the Philippine map (figure 2), plot the location of the following volcanoes. Use the colors indicated in the legend. 4. It is an element that doesn't have the characteristics of metal. 5. It is an element that having the nature of metal. 9. A place that is disorderly …. Circle the correct choice within the parenthesis for Circle the correct choice within the parenthesis for 1 -18. 1. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucleus. 2. mRNA is made during (transcription/translation). 3. mRNA is made in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 4. DNA is located in the (nucleus/cytoplasm) 5. (Translation/Transcription) converts DNA into mRNA. 6.
Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJUS A nucleotide is an organic molecule with a basic composition of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and phosphate. DNA and RNA are polynucleotides, which contain a chain of nucleotides monomers with different nitrogenous bases. Nucleotides are essential for carrying out metabolic and physiological activities. 3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected Nucleotides in DNA and RNA Both deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: Nitrogenous Base Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. transcription and translation Flashcards - Quizlet 1. draw a DNA and RNA nucleotide. look aT SHEET 2. What are the differances between DNA and RNA? a) there are deoxiribos b)there is ribos sugar in RNA c)there is thymen in DNA and uricil in RNA d)DNA double helix & RNA single strond 3. What is the point of replication? replication fork (to make DNA) 4. When & where does replication occur?
Draw a DNA nucleotide an RNA nucleotide Label each of the 3 major parts ... Draw a DNA nucleotide & an RNA nucleotide. Label each of the 3 major parts. 2. What are the three major differences between DNA & RNA? 3. What is the purpose of DNA replication? ____________________________ 4. When & where does replication occur? _____________________________ 5.
2.6: DNA and RNA Flashcards | Quizlet Identify and label carbons by number (for example, C1, C2, C3) on a nucleotide drawing. Understanding: The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides. The carbons of the sugar component of the nucleotide are numbers clockwise, starting from the oxygen in the ring at the top and the phosphate group to the left.
Name part d circle the correct choice within the - Course Hero 3. mRNA is made in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 4. DNA is located in the (nucleus/cytoplasm) 5. (Translation/Transcription) converts DNA into mRNA. 6. (mRNA/rRNA) is used to carry the genetic code from DNA to the ribosomes. 7. (tRNA/rRNA) makes up the ribosome. 8. (DNA/RNA) uses uracil instead of thymine. 9. (RNA/amino) acids make up a protein. 11.
/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)
/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)
Post a Comment for "44 draw a dna nucleotide and an rna nucleotide label each of the 3 major parts"