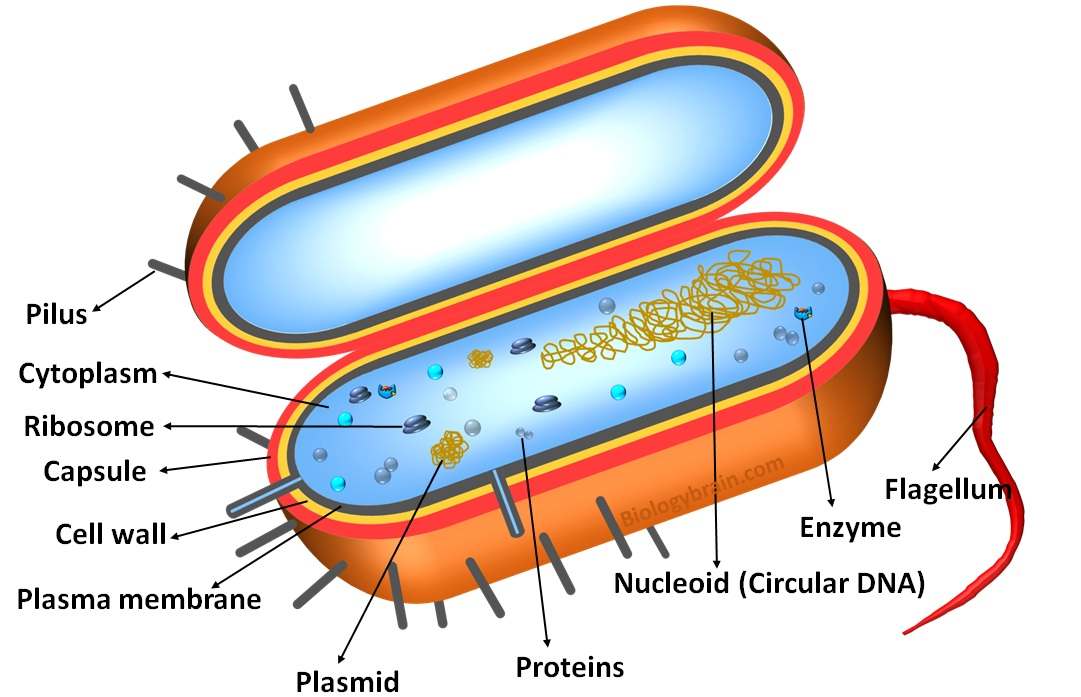
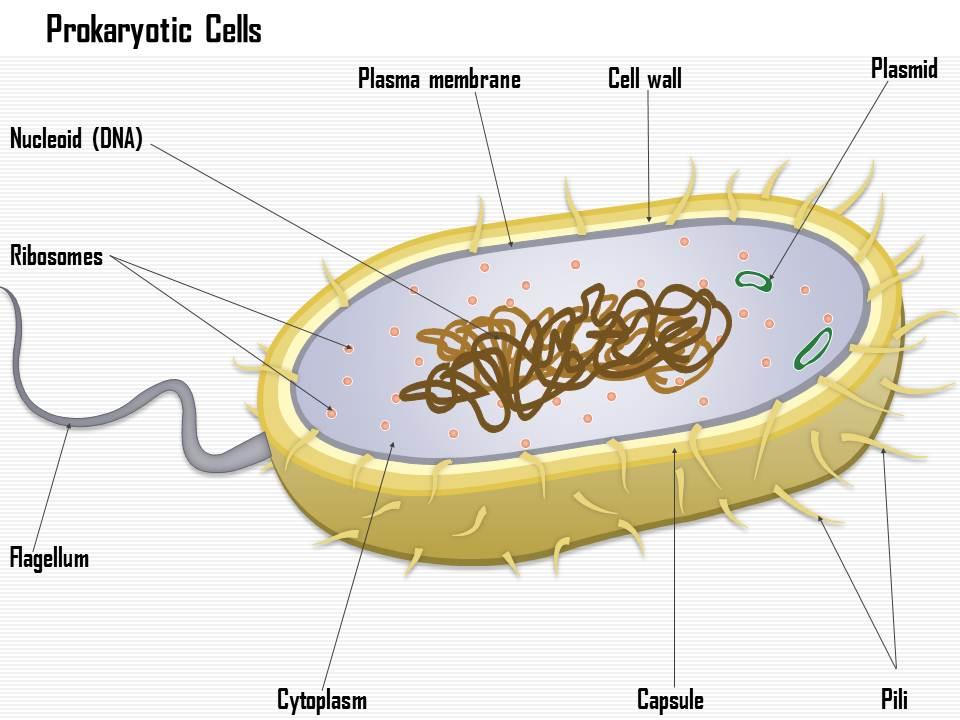
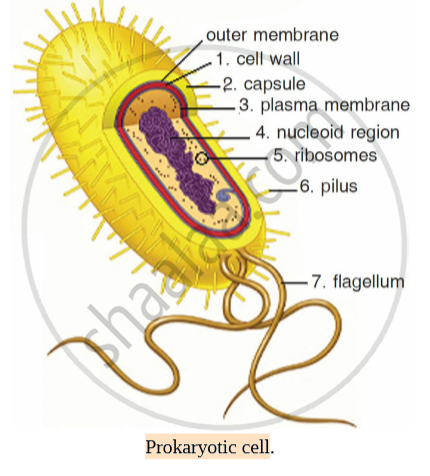
44 prokaryotic cell label
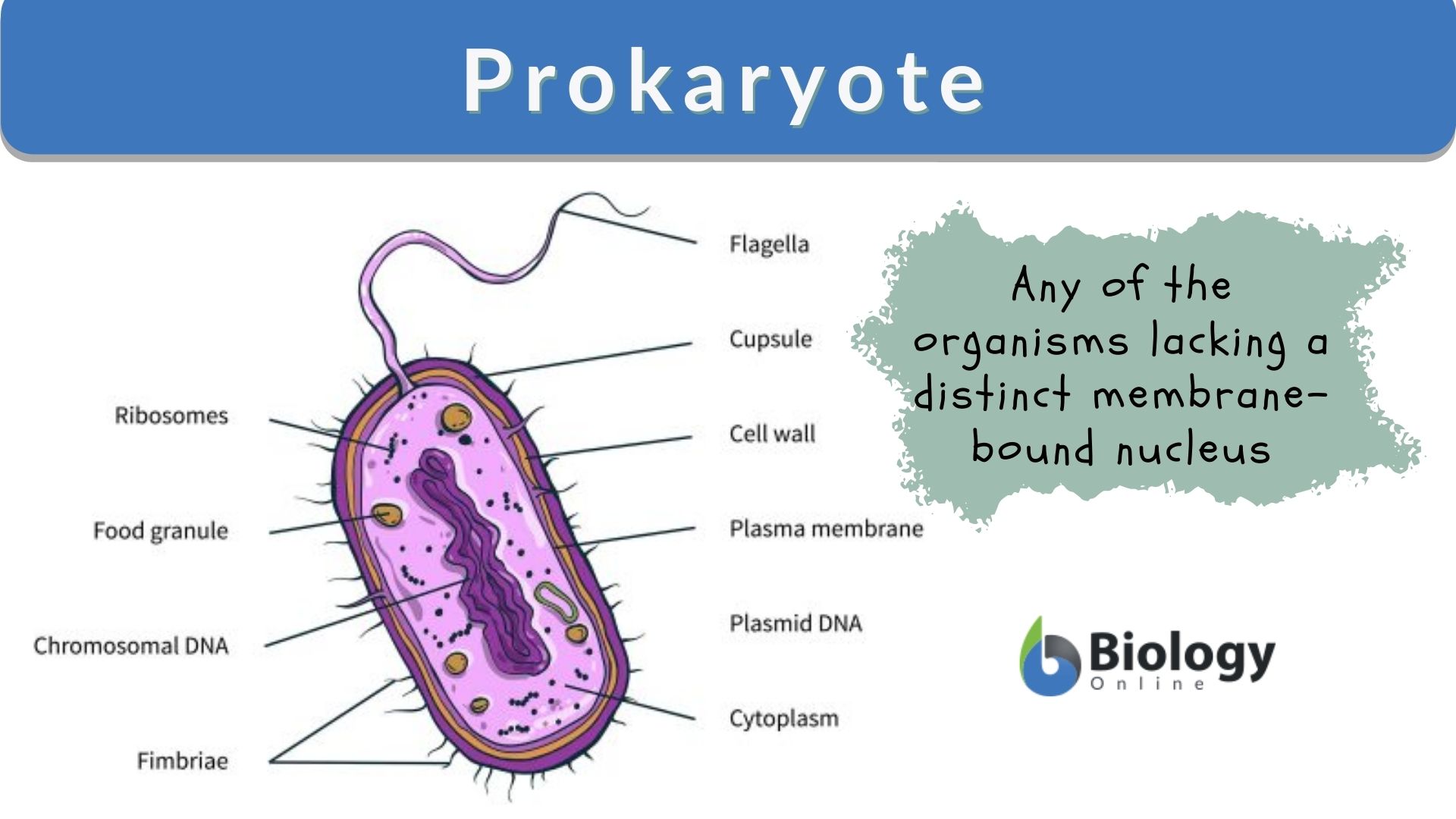
Prokaryotic Cell: Definition, Characteristics, Diagram & Structure Prokaryotic cell s are single-celled organisms that lacks a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. What is a Prokaryotic Cell? Prokaryotic cells are microorganisms that are known to be the earliest on earth. Kingdom Monera includes the prokaryotic cells. A teaspoon full of rich soil may contain billions of them. Parts of the Prokaryotic Cell and their Functions - Postposmo Prokaryotic cell. The prokaryotic cell is the most elementary cell of the tree of life. As they do not have a nucleus, they are called prokaryotic, which comes from the conjunction of two Greek terms, pro, which means prior or before; and karyon which means nut or nucleus, so the name prokaryote literally means before or prior to the nucleus and can be related to the Origin of life.
Prokaryotic Cells: Definition, Structure, Function (with Examples) Scientists believe that prokaryotic cells were some of the first life forms on Earth. These cells are still abundant today and can be divided into bacteria and archaea. A classic example of a prokaryotic cell is Escherichia coli (E. coli). Prokaryotic cells are fundamental to mastering high school cell biology.
Prokaryotic cell label
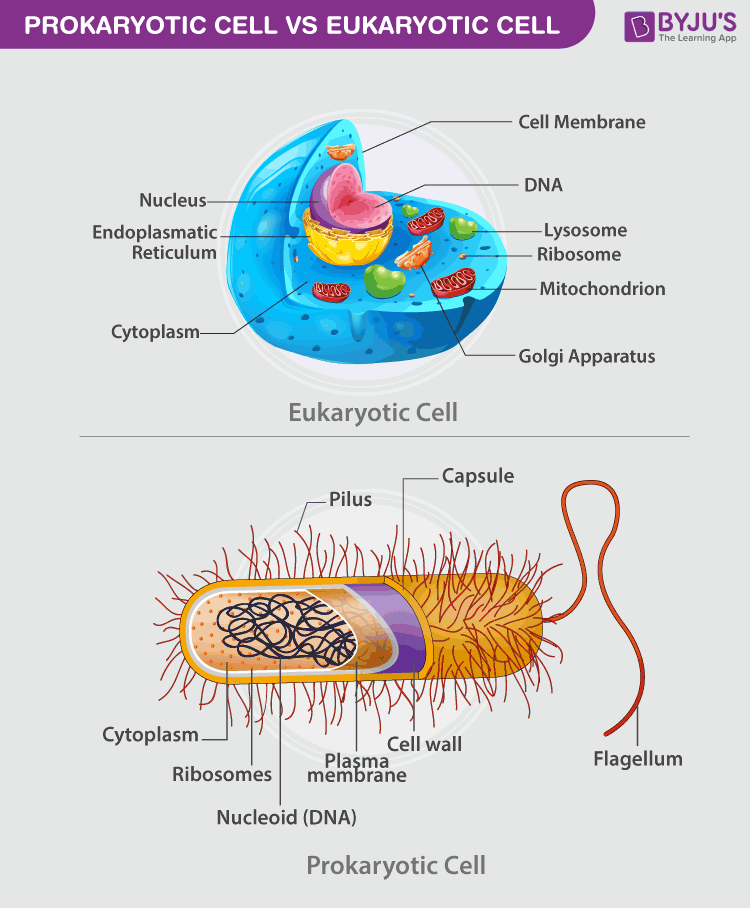
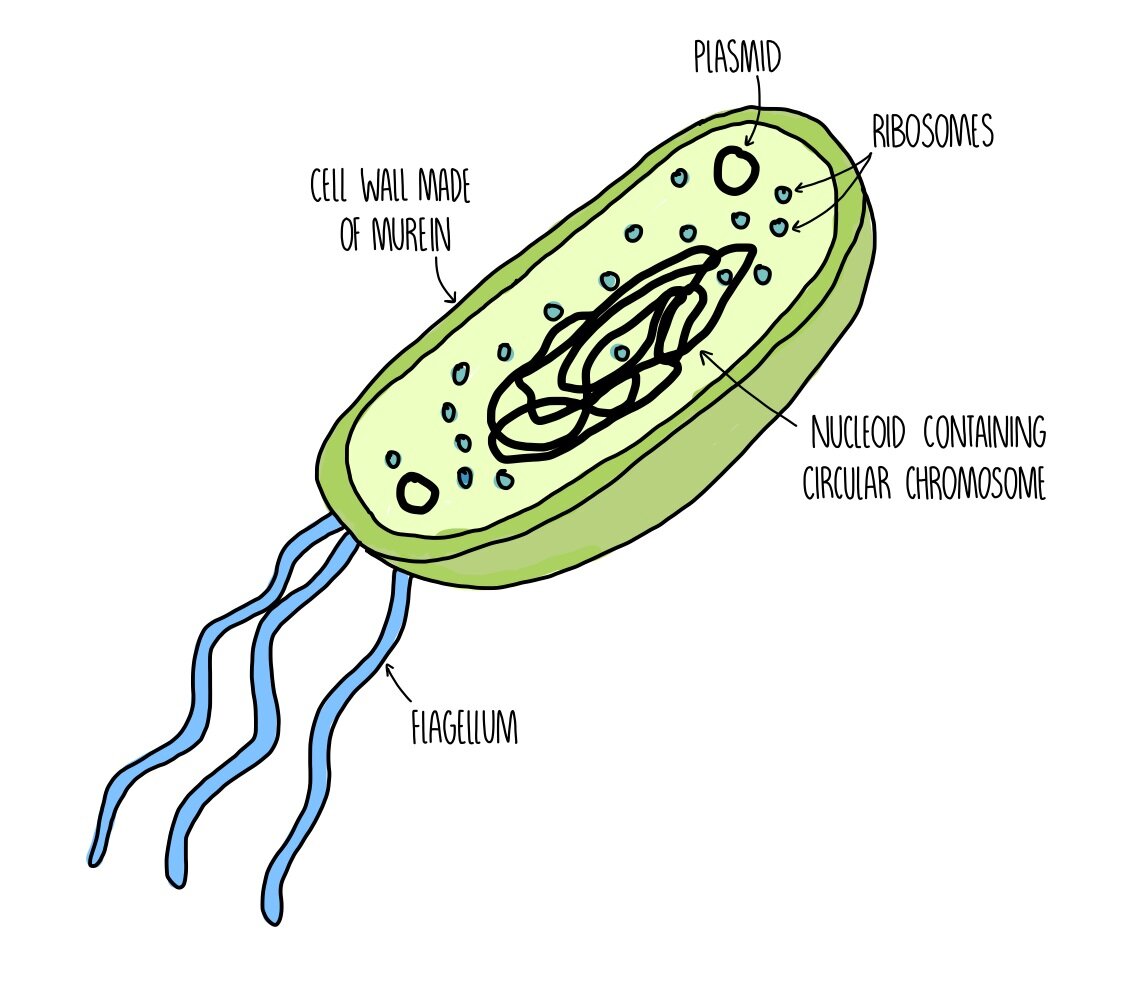
Prokaryotic Cells- Definition, Structure, Characteristics, and ... - BYJUS The prokaryotic cells have four main components: Plasma Membrane- It is an outer protective covering of phospholipid molecules which separates the cell from the surrounding environment. Cytoplasm- It is a jelly-like substance present inside the cell. All the cell organelles are suspended in it. DNA- It is the genetic material of the cell. Prokaryotic Cells: Structure, Function, and Definition - ThoughtCo Prokaryotic cells lack organelles found in eukaryoitic cells such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticuli, and Golgi complexes. According to the Endosymbiotic Theory, eukaryotic organelles are thought to have evolved from prokaryotic cells living in endosymbiotic relationships with one another. Like plant cells, bacteria have a cell wall. Prokaryotic Cells - Visible Body Prokaryotic cells are normally smaller than eukaryotic cells, with a typical size range of 0.1 to 5 μm in diameter. Prokaryotes are made up of a single cell, though they can pair up or cluster together to form mats. 2. Structures on the outside of a bacterium protect it and help it move. Like all other cells, bacteria have a cell membrane and ...
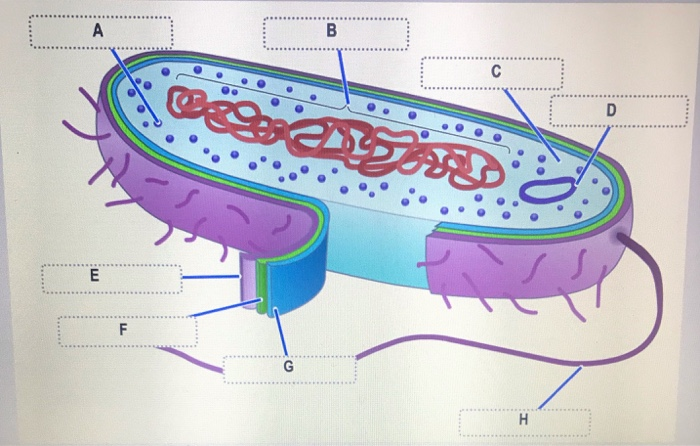
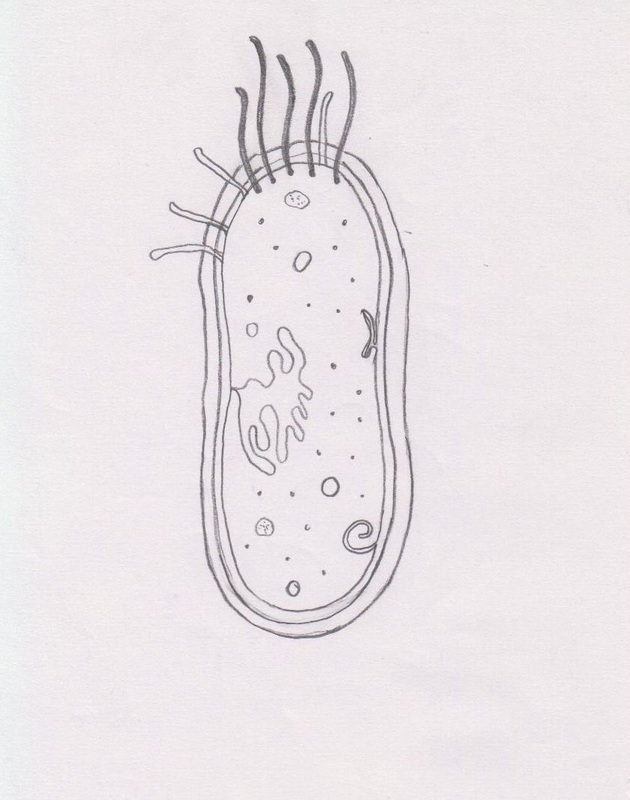
Prokaryotic cell label. Solved: Label the parts of the prokaryotic cell. Label ... | Chegg.com Label the parts of the prokaryotic cell. Step-by-step solution Step 1 of 4 Cells without the presence of nucleus are called prokaryocytes (Greek: pro, before and karyon, nucleus). Chapter 3, Problem 42CT is solved. View this answer View a sample solution Step 2 of 4 Step 3 of 4 Step 4 of 4 Back to top Corresponding textbook Label the prokaryotic cell Quiz - PurposeGames.com Label the prokaryotic cell by blueseas 6,336 plays 8 questions ~20 sec English More 0 too few (you: not rated) Tries 8 [?] Last Played February 22, 2022 - 12:00 am There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. Remaining 0 Correct 0 Wrong 0 Press play! 0% 08:00.0 Highscores Show More How to draw a prokaryotic cell | prokaryotic organism | Bacterial cell ... Hello friends!!!!In this video, I will be showing you that how to draw "A prokaryotic cell" very easily.Please like, share and subscribe!!! ️ ️ ️ And do tell... Prokaryote - Wikipedia Prokaryote. Diagram of a typical prokaryotic cell. A prokaryote ( / proʊˈkærioʊt, - ət /) is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. [1] The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό ( pro, 'before') and κάρυον ( karyon, 'nut' or 'kernel').
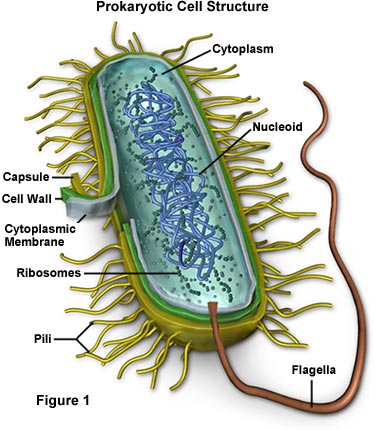
Prokaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram - Science Prof Online Prokaryotic cells are much simpler than the more evolutionarily advanced eukaryotic cell . Whereas eukaryotic cells have many different functional compartments, divided by membranes, prokaryotes only have one membrane (the plasma membrane) enclosing all of the cell's internal contents. Prokaryotic_and_eukaryotic_cells_lab_handout.docx - Course Hero Name: Date: Biology Lab Activities: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab 3: Compare Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Refer to your labeled bacteria, animal, and plant cells from Labs 1 and 2, as well as the 3D bacteria, animal, and plant cells on the Visible Body Biology Learn Site, to help you answer the following questions comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic Cell - Definition, Examples & Structure - Biology Dictionary Prokaryotic cells are usually between 0.1 to 5 micrometers in length (.00001 to .0005 cm). Eukaryotic cells are generally much larger, between 10 and 100 micrometers. Prokaryotic cells have a higher surface-area-to-volume ratio because they are smaller, which makes them able to obtain a larger amount of nutrients via their plasma membrane. 4.2: Prokaryotic Cells - Biology LibreTexts Prokaryotes are predominantly single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea. All prokaryotes have plasma membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA that is not membrane-bound. Most have peptidoglycan cell walls and many have polysaccharide capsules. Prokaryotic cells range in diameter from 0.1 to 5.0 μm.
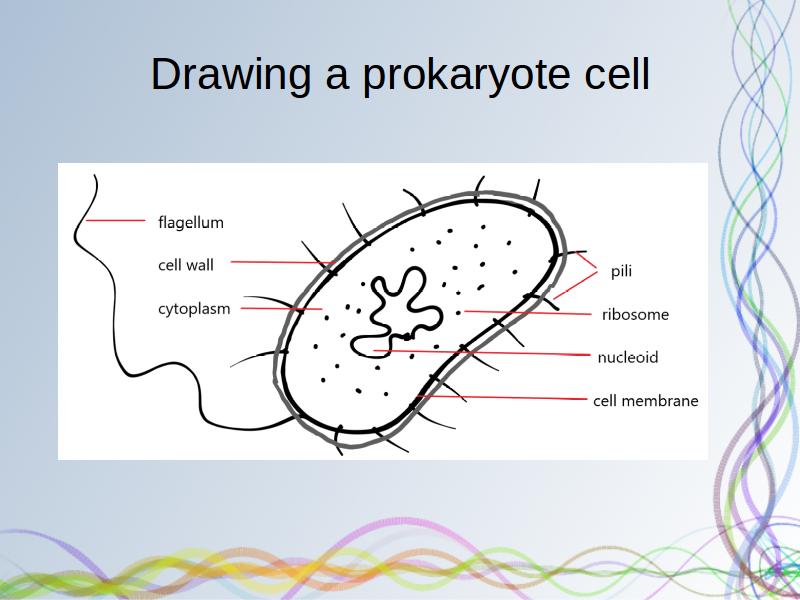
Prokaryotic cells (article) | Khan Academy Typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in diameter and are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which usually have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 μm. The figure below shows the sizes of prokaryotic, bacterial, and eukaryotic, plant and animal, cells as well as other molecules and organisms on a logarithmic scale. Eukaryotic Cell Labeled Diagram | Quizlet Contains most of the DNA that controls the cell. Rough endoplasmic reticulum a network of double membranes; attached to the outside of the membranes synthesize proteins that are moved into the cisternal space where carbohydrates are added to make glycoproteins. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum a network of double membranes; no ribosomes are attached Prokaryotic Cell Structure, Characteristics & Function - Lab-Training.com Structure and Function of Prokaryotic Cells. Prokaryotic cells fall into a size range of about 1-5µm and hence can be observed clearly by microscopes. However, some prokaryotic cells may be larger than this. A prokaryotic cell contains external and internal structures. Capsule, flagella, axial filaments, fimbriae, and pili are present ... IB Biology Notes - 2.2 Prokaryotic cells - IB Guides Prokaryotic cells 2.2.1 Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of Escherichia coli (E. coli) as an example of a prokaryote.. 2.2.2 Annotate the diagram from 2.2.1 with the functions of each named structure.. Cell wall: Protects the cell from the outside environment and maintains the shape of the cell.It also prevents the cell from bursting if internal pressure rises.
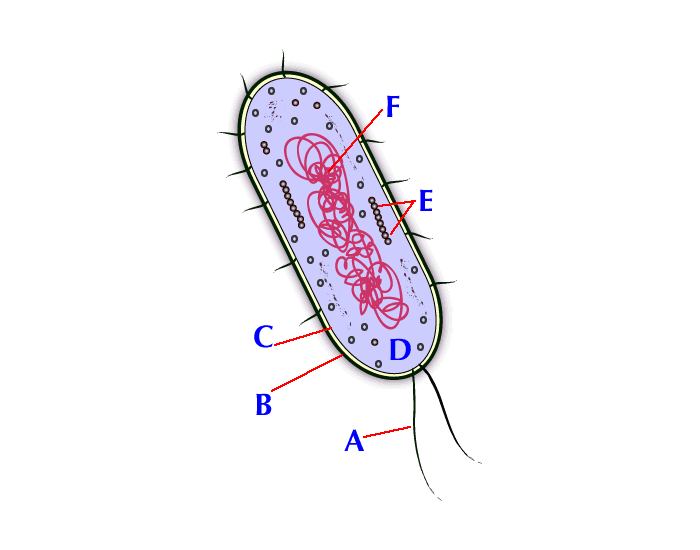
Label a prokaryote worksheet Label a prokaryote prokaryote label ID: 2505341 Language: English School subject: Biology Grade/level: 9-12 Age: 14-18 Main content: Cells Other contents: label Add to my workbooks (10) Download file pdf Embed in my website or blog Add to Google Classroom Add to Microsoft Teams Share through Whatsapp Link to this worksheet: Copy cohenbio Finish!!
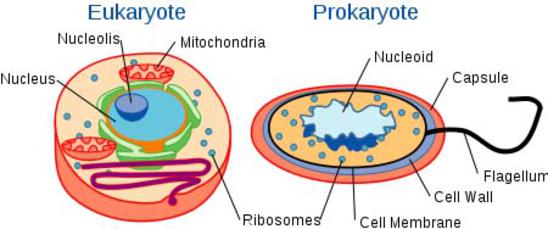
Eukaryotic cell diagram labelling game - ESL Games Plus All of these organisms have eukaryotic cells, which mean they contain membrane-bound organelles that their prokaryotic rivals sadly lack. Organelles and everything else inside the cell swim in a gelatin-like fluid known as cytoplasm. The outside of the cell is protected by a plasma membrane.
Eukaryotic Cell - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells found in ...
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells: Similarities & Differences Prokaryotes are bacteria and archaea. TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read) Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are either archaea or bacteria. Their cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes include larger, more complex organisms such as plants and animals. Only eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus.
Prokaryote structure (article) | Khan Academy Key points: Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms belonging to the domains Bacteria and Archaea. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, have no nucleus, and lack organelles. All prokaryotic cells are encased by a cell wall. Many also have a capsule or slime layer made of polysaccharide.
Prokaryotic Cell Labeling Diagram | Quizlet A non-membrane-bounded region in a prokaryotic cell where the DNA is concentrated. cytoplasm A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended capsule Covers the cell wall in prokaryotes. cytoplasmic membrane a semipermeable barrier that separates the cell interior (cytoplasm) from the environment cell wall
Prokaryotic Cells Quiz - ProProfs Quiz Prokaryotic cells are unicellular organisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle. They are divided into two domains; Archaea and Bacteria. What do you know about this particular organism? Let's find out with this amazing quiz right here right now. We wish you all the best to you. Have fun!
Solved Prokaryotic cell Label the image to assess your - Chegg Nursing questions and answers. Prokaryotic cell Label the image to assess your understanding of prokaryotic cell structure. Nucleoid A Plasma membrane Fimbriae Nuk Glycocalyx Slace < Prev 3 of 12 Next > Search search o 11 ED Saved ma Grane Nucleoid abnae cocalyx Cytoplasm Flagella Coll wall Coll wall Ribosomes Plasma < Prev 3 of 12 Next > 361 ...
Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells - BYJUS A prokaryotic cell is a primitive type of cell that is characterized by the absence of a nucleus. Furthermore, prokaryotes do not possess membrane-bound cellular organelles. Prokaryotes are exclusively unicellular. What is a Eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles.
Prokaryotic cell to label - Labelled diagram - Wordwall Prokaryotic cell to label - Labelled diagram Home Features Contact Price Plans Log In Sign Up Language nucleoid region, pili, ribosomes, flagellum, plasmid, cytoplasm, plasma membrane, cell wall, capsule. Prokaryotic cell to label Share by Susanmgillen KS5 Biology Like Edit Content More Leaderboard Switch template Interactives
2.3: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells - Biology LibreTexts Prokaryotic cells are cells without a nucleus. The DNA in prokaryotic cells is in the cytoplasm rather than enclosed within a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms, such as bacteria, like the one shown in Figure below. Organisms with prokaryotic cells are ca lled prokaryotes.
Prokaryotic Cells - Visible Body Prokaryotic cells are normally smaller than eukaryotic cells, with a typical size range of 0.1 to 5 μm in diameter. Prokaryotes are made up of a single cell, though they can pair up or cluster together to form mats. 2. Structures on the outside of a bacterium protect it and help it move. Like all other cells, bacteria have a cell membrane and ...
Prokaryotic Cells: Structure, Function, and Definition - ThoughtCo Prokaryotic cells lack organelles found in eukaryoitic cells such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticuli, and Golgi complexes. According to the Endosymbiotic Theory, eukaryotic organelles are thought to have evolved from prokaryotic cells living in endosymbiotic relationships with one another. Like plant cells, bacteria have a cell wall.
Prokaryotic Cells- Definition, Structure, Characteristics, and ... - BYJUS The prokaryotic cells have four main components: Plasma Membrane- It is an outer protective covering of phospholipid molecules which separates the cell from the surrounding environment. Cytoplasm- It is a jelly-like substance present inside the cell. All the cell organelles are suspended in it. DNA- It is the genetic material of the cell.
























Post a Comment for "44 prokaryotic cell label"